Plastic Stent
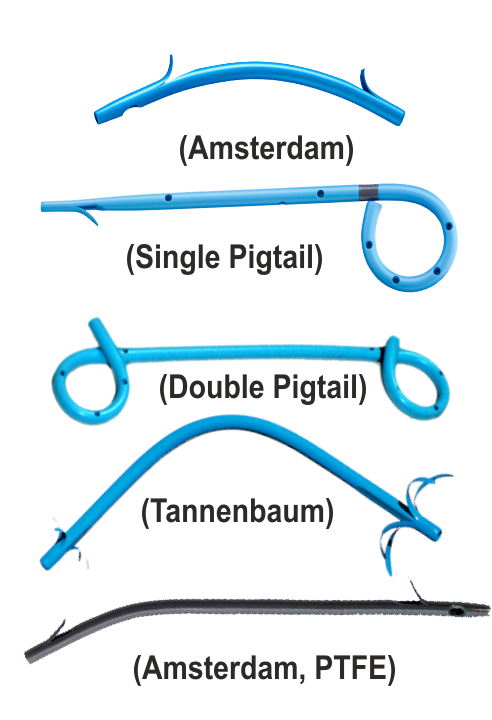
Plastic stents are tubular devices used primarily to establish patency in obstructed bile or pancreatic ducts. They are made from materials such as polyethylene, polyurethane, or Teflon, and come in various configurations to suit different clinical needs.
Key Features of Plastic Stents
Materials: Commonly made from polyethylene, polyurethane, or Teflon.
Diameter and Length: Available in diameters ranging from 5F to 12F and lengths from 1 to 18 cm.
Design: Available in straight, angled, or curved shapes with single or multiple flaps, and may include side holes to enhance drainage.
Types: Include pigtail stents, flanged stents (e.g., Tannenbaum design), and double-layer stents.
Advantages
Effective Drainage: Provides reliable biliary drainage, improving patient outcomes by relieving jaundice and reducing the risk of cholangitis.
Minimally Invasive: Offers a less invasive alternative to surgical interventions, reducing recovery time and complications.
Plastic stents are widely used due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, though they generally have shorter patency times.
